Iron In Tampa Water & Rusty Stains
Iron is a mineral that all bodies need to function — but in elevated levels, it can pose health risks and cause potential damage to your home. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classifies iron as a secondary contaminant, meaning it doesn’t typically present immediate health concerns like lead or radiological contaminants, but it can affect the taste, color, and smell of your tap water, along with causing long-term issues like damage to plumbing and appliances.
If you live in Tampa Bay, the presence of iron and other common contaminants in your drinking water depends on whether you use public water systems or private wells. Either way, iron is one of many drinking water contaminants worth keeping an eye on.
Why Choose Culligan for Iron Removal in Tampa?
Rust stains, metallic tastes, and clogged plumbing are common signs of excess iron—and Tampa Culligan has the specialized solutions to stop the damage before it spreads. From advanced iron filters like the Iron-Cleer® system to high-performance water softeners for clear-water iron, our systems are engineered to tackle Tampa’s unique water challenges. With free water testing, custom treatment plans, and local expertise across Hillsborough County and beyond, Culligan helps restore the quality, taste, and reliability of the water flowing through your home.
Solutions
Products to Remove Iron & Rust Stains

Aquasential™ Smart High Efficiency Water Softener
- Smart brine tank auto-monitors salt levels
- Convenient auto-bypass valve
- Reliable non-corrosive valve
- Worry-free maintenance

Aquasential™ Smart High Efficiency Whole House Water Filters
Reduce sediments in your water and contaminants that cause your water to appear, taste, and smell unpleasant. Your system can also lessen the taste and odor of chlorine, and prevent pipe damage and staining from low pH water. Additional customizations include:
- Culligan® Filtr-Cleer® Water Filters – Reduces Sediment Problems
- Culligan® Cullar® Water Filters – Reduces Taste and Odor Problems
- Culligan® Cullneu Water Filters – Reduces Acid Problems
Iron Levels in Tampa Bay Water
The municipal water supply in Tampa Bay is managed by Tampa Bay Water and is treated at a water treatment plant to maintain safe, high-quality drinking water. According to the annual water quality report, Tampa’s public water utilities aim to stay below the EPA’s maximum contaminant level (MCL) for iron — 0.3 mg/L — which was established for aesthetic rather than health purposes. However, Tampa’s source water, which comes from both surface water sources and underground aquifers, may still contain elevated levels of iron due to natural filtration processes, urban runoff, and mineral content in the Floridan Aquifers.
Unfortunately, the City of Tampa Water Department doesn’t consistently include iron concentrations in its drinking water quality report, so the best way to determine whether you have clear-water iron (also known as ferrous iron) or other types of iron in your potable water is with an independent water test.
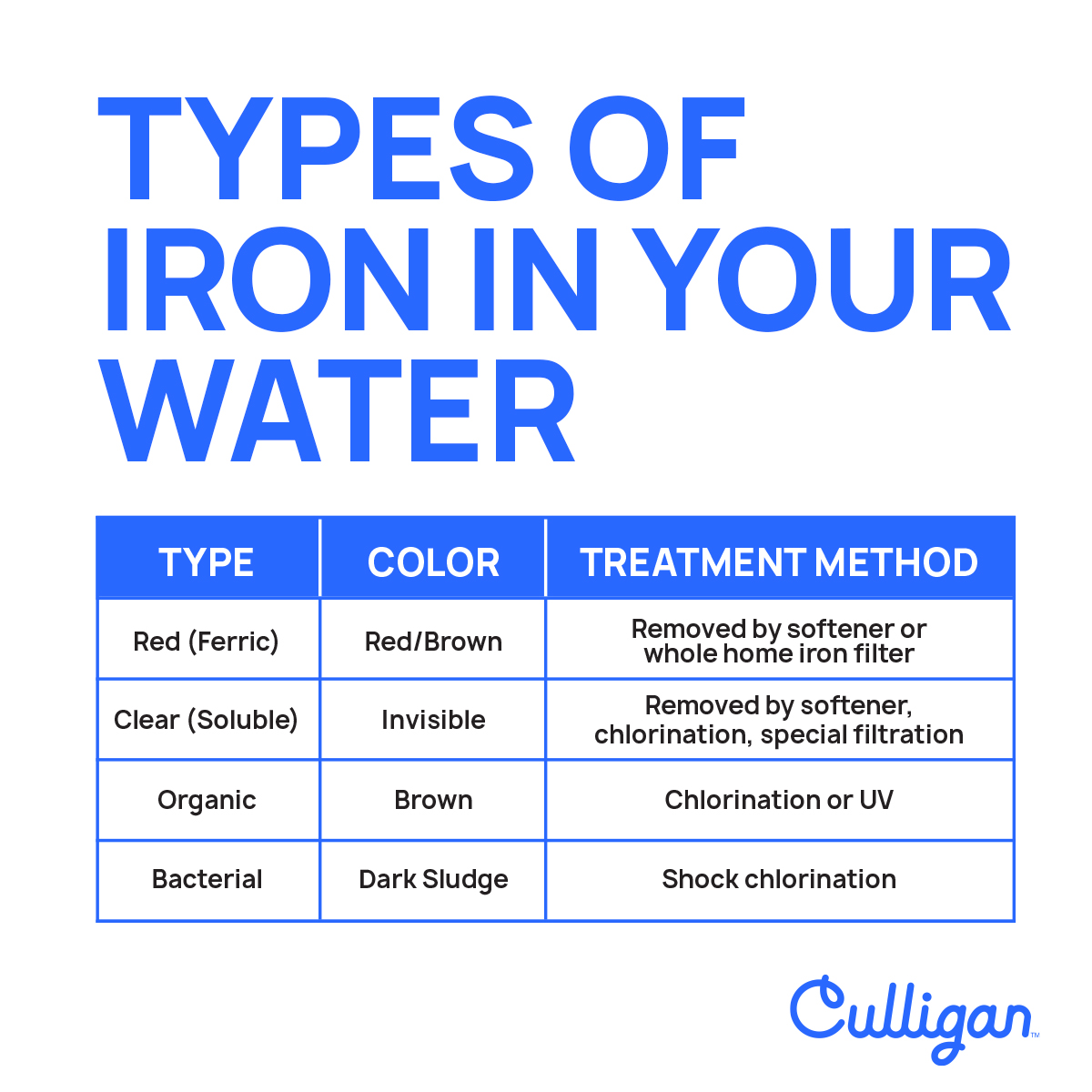
Four Types Of Iron
Understanding the different types of iron found in Tampa’s water, their potential impacts, and effective solutions can help homeowners mitigate damage and maintain a clean, pristine living environment.
Red Iron
Ferric “insoluble” iron is visible to the naked eye and can cause a number of issues with your home, as well as in your food and drink. Red water iron can be removed by a water softener, but a more common treatment is an iron filter, which Culligan offers as a part of its whole home solutions. The state-of-the-art Iron-Cleer® water conditioning system solves iron and rust staining, leaving you with nothing but clean water in your sinks, fixtures, dishes and clothes.
Clear Iron
Ferrous “soluble” iron is an invisible dissolved solid that can appear after coming out of your faucet. This type of water is low on oxygen and typically comes from deeper wells and groundwater sources.
The most common way to treat clear iron is with a Culligan Water Softener, which can remove clear-water iron through ion exchange, particularly if your home’s water supply has a low pH. Other options, such as chlorination and manganese greensand filtration require maintenance and the proper amount of pressure.
Organic Iron
Generally, organic iron is pure iron combined with any dissolved organic matter in the water, such as tannins. A tannin is a biomolecule produced by vegetation that stains liquids, including tea and coffee. When tannins react with water containing iron, it creates a black residue. This usually occurs in shallow wells that are affected by groundwater.
Iron Bacteria
Iron bacteria are naturally occurring organisms in soils and groundwater that feed off iron, leaving waste deposits. They leave behind a dark sludge that sticks to pipes and fixtures, particularly in your water and toilet tanks and plumbing fixtures. The microorganisms also can lead to bad tasting and odorous water. You can physically remove the sludge from your toilet tank or use “shock” chlorination methods, but this is merely a temporary solution. The only way to reduce the amount of iron bacteria is to reduce the amount of iron itself.
How Can Iron Invade Your Well Water?
Iron can invade your well water through several natural and environmental processes:
- Natural soil and rock: Tampa’s geology contributes to iron-rich mineral content in groundwater.
- Corroded plumbing: Iron pipes can rust, releasing flakes into your heated water and cold water lines.
- Rainwater infiltration: Surface water runoff from industrial waste or urban areas can carry iron into aquifers.
- Groundwater movement: As rainwater and snowmelt seep through the soil, they absorb minerals like iron.
- Iron bacteria: These microbes flourish in iron-rich environments, further degrading water quality.
Collectively, these factors can result in elevated levels of iron in well water, leading to various issues such as staining, metallic tastes, and potential damage to plumbing and appliances.
Harmful Effects Of Iron In Your Home
Even if iron doesn’t breach federal regulations for toxicological review, it can wreak havoc on your home:
Gardening issues: Iron-rich water can stain sidewalks and alter soil pH, affecting plant health.
Staining: Rust marks on porcelain, toilets, sinks, and clothing.
Taste and Odor: A metallic taste in your beverages or food can be caused by high iron levels and disinfection byproducts like Haloacetic Acids.
Clogging: Limescale buildup and iron sludge can block pipes, pumps, and appliances.
Appliance inefficiency: Long-term exposure to iron can reduce the lifespan and efficiency of dishwashers, washing machines, and water heaters, increasing energy costs.
Is Iron in Water a Health Concern?
While iron isn’t classified among harmful contaminants at low levels, chronic exposure or long-term ingestion can contribute to intestinal tumors, neurological issues, and aggravate conditions like hemochromatosis. Studies have suggested a possible link between high iron levels and bone cancer, especially with unregulated contaminants and treatment byproducts such as dichloroacetic acid or Ethylene Dibromide.
Populations like pregnant women, infants, and those with compromised immune systems may be more sensitive to levels in drinking water that exceed Health Advisory Levels or EWG-selected health guidelines. Some experts believe there’s no truly safe tap water level for iron when combined with other contaminants like arsenic (measured in ppb for arsenic) or PFAS.
Iron Water Treatment for Tampa Residents
The best way to ensure tap water safety is to invest in Water Filters and Water Filtration systems designed for Tampa Bay’s water quality issues. Culligan offers custom solutions for your zip code using carbon water filters, iron filters, and water conditioners tailored to combat Tampa’s unique range of contaminants.
Water softeners are highly effective for ferrous iron, while iron filters like the Iron-Cleer® system are ideal for ferric iron. These systems work together to improve drinking water quality, protect your plumbing, and restore a much-improved taste sensation in every glass.
Want to Know What’s in Your Tampa Tap Water?
If you’re unsure about the levels of contaminants in your home’s water, request a free water test from Culligan. Our local experts in Hillsborough County, Plant City, and throughout South Florida offer benchmark testing, PFAS Testing and Guidance, and custom filtration recommendations based on your area’s History database and annual utility averages.
Don’t let iron and other contaminants in tap water ruin your home. Get your water tested and find out how Culligan’s filtration systems can help you achieve clean water that’s safe for every member of your family.

Facebook